CRM with Role-Based Access: Securing Data, Empowering Users, and Driving Business Growth
In today’s dynamic business landscape, Customer Relationship Management (CRM) systems have become indispensable tools for organizations aiming to build stronger customer relationships, streamline operations, and boost revenue. However, the effectiveness of a CRM hinges not only on its features but also on how well it’s secured and how efficiently users can access the data they need. This is where the concept of Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) comes into play, transforming CRM into a powerful, secure, and user-friendly platform.
What is Role-Based Access Control (RBAC)?
RBAC is a security mechanism that restricts system access to authorized users based on their specific roles within an organization. Instead of granting individual permissions to each user, RBAC assigns roles that define the level of access a user has to different parts of the system. These roles are then associated with specific permissions, determining what actions a user can perform, such as viewing, creating, editing, or deleting data.
Think of it like a keycard system in a large office building. Each employee receives a keycard (role) that allows them access to certain floors and rooms (data and functionalities) based on their job responsibilities. A marketing intern might only have access to marketing-related data, while a sales manager would have broader access to sales opportunities, customer accounts, and reports.
Why is RBAC Important in CRM?
RBAC is not merely a security feature; it’s a cornerstone of effective CRM implementation. Here’s why it’s crucial:
- Enhanced Data Security: CRM systems contain sensitive customer information, including contact details, purchase history, financial data, and communication records. RBAC ensures that only authorized personnel can access this data, preventing unauthorized access, data breaches, and potential compliance violations.
- Improved Data Integrity: By limiting access to data modification based on roles, RBAC helps maintain data accuracy and consistency. For example, only authorized sales representatives can update opportunity stages, preventing accidental or malicious alterations by users in other departments.
- Streamlined User Experience: RBAC simplifies the user experience by providing users with access only to the features and data they need to perform their job. This reduces clutter, improves navigation, and enhances overall productivity.
- Simplified Administration: Managing user permissions can be a complex and time-consuming task, especially in large organizations. RBAC simplifies administration by allowing administrators to assign roles to users rather than configuring individual permissions.
- Compliance with Regulations: Many industries are subject to strict data privacy regulations, such as GDPR, HIPAA, and CCPA. RBAC helps organizations comply with these regulations by ensuring that sensitive data is protected and accessed only by authorized individuals.
- Enhanced Collaboration: RBAC can facilitate collaboration by allowing users to share data and insights with colleagues who have the appropriate roles and permissions. This promotes teamwork and improves decision-making.
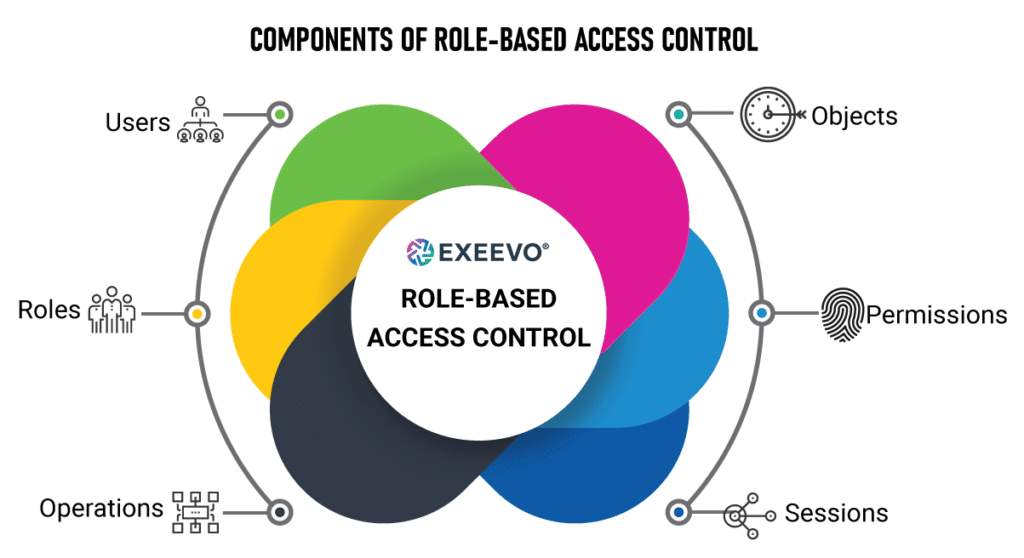
How RBAC Works in CRM: Key Components
A well-implemented RBAC system in CRM typically consists of the following key components:
- Roles: These are predefined categories that represent different job functions or responsibilities within the organization, such as Sales Representative, Marketing Manager, Customer Service Agent, or Administrator.
- Permissions: These define the specific actions that users can perform within the CRM system, such as viewing customer records, creating new opportunities, editing contact information, or generating reports.
- Users: These are individual employees or system users who are assigned one or more roles based on their job responsibilities.
- Role-Permission Mapping: This is the process of associating specific permissions with each role, defining the level of access that users with that role will have to different parts of the CRM system.
- User-Role Assignment: This is the process of assigning roles to individual users based on their job responsibilities.
- Access Control Engine: This is the core component of the RBAC system that enforces access control policies by verifying a user’s role and permissions before granting access to specific data or functionalities.
Implementing RBAC in Your CRM: Best Practices
Implementing RBAC in your CRM system requires careful planning and execution. Here are some best practices to follow:
-
Define Clear Roles: Start by defining clear and well-defined roles that align with your organization’s structure and job functions. Consider the specific responsibilities of each role and the level of access required to perform those responsibilities effectively.
-
Granular Permissions: Define granular permissions that control access to specific data elements and functionalities within the CRM system. This allows you to fine-tune access control policies and ensure that users have only the access they need.
-
Least Privilege Principle: Adhere to the principle of least privilege, which states that users should be granted only the minimum level of access necessary to perform their job duties. This minimizes the risk of unauthorized access and data breaches.
-
Regular Audits: Conduct regular audits of user roles and permissions to ensure that they are still appropriate and aligned with current job responsibilities. Remove or modify roles and permissions as needed to maintain data security and compliance.
-
User Training: Provide comprehensive training to users on how to use the CRM system and understand their assigned roles and permissions. This helps prevent accidental errors and ensures that users are aware of their responsibilities regarding data security.
-
Documentation: Maintain detailed documentation of your RBAC implementation, including role definitions, permission assignments, and access control policies. This documentation will be invaluable for troubleshooting, auditing, and compliance purposes.
-
Integration with Other Systems: If your CRM system is integrated with other business applications, such as ERP or marketing automation platforms, ensure that RBAC is consistently enforced across all integrated systems.
Benefits of RBAC: A Summary
In summary, implementing RBAC in your CRM system offers a wide range of benefits:
- Stronger Security: Protects sensitive customer data from unauthorized access.
- Improved Data Integrity: Ensures data accuracy and consistency.
- Enhanced User Experience: Simplifies access to relevant features and data.
- Streamlined Administration: Simplifies user permission management.
- Compliance: Helps meet data privacy regulations.
- Better Collaboration: Facilitates secure data sharing and teamwork.
- Increased Productivity: Empowers users with the right tools and access.
Conclusion
In today’s data-driven world, CRM systems are essential for businesses seeking to build strong customer relationships and drive growth. However, the effectiveness of a CRM depends on its security and user-friendliness. RBAC provides a robust mechanism for securing data, empowering users, and simplifying administration, making it an indispensable feature for any modern CRM system. By implementing RBAC effectively, organizations can ensure that their CRM is a powerful and secure tool that supports their business goals while protecting sensitive customer data.